ALOPECIA
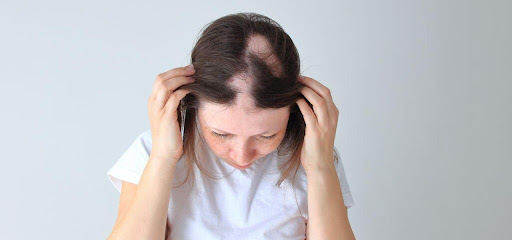
Alopecia Areata is a type of autoimmune condition, the body rejects the hair follicles for an unknown reason. It usually appears suddenly as round patches of hair loss on the scalp. Alopecia Totalis is when all the hair on the scalp is lost and Alopecia Universalis is when all body hair is lost. Alopecia Areata is not contagious, is not caused by foods, nor is the result of nervousness. It occasionally runs in families. Alopecia Areata has three stages. First, there is sudden hair loss. Then, the patches of hair loss may enlarge. Lastly, new hair grows back. This may takes months and sometimes more than a year.
SCHEDULE A CONSULTATION
If you’re thinking about next steps, get in touch to schedule a consultation.


