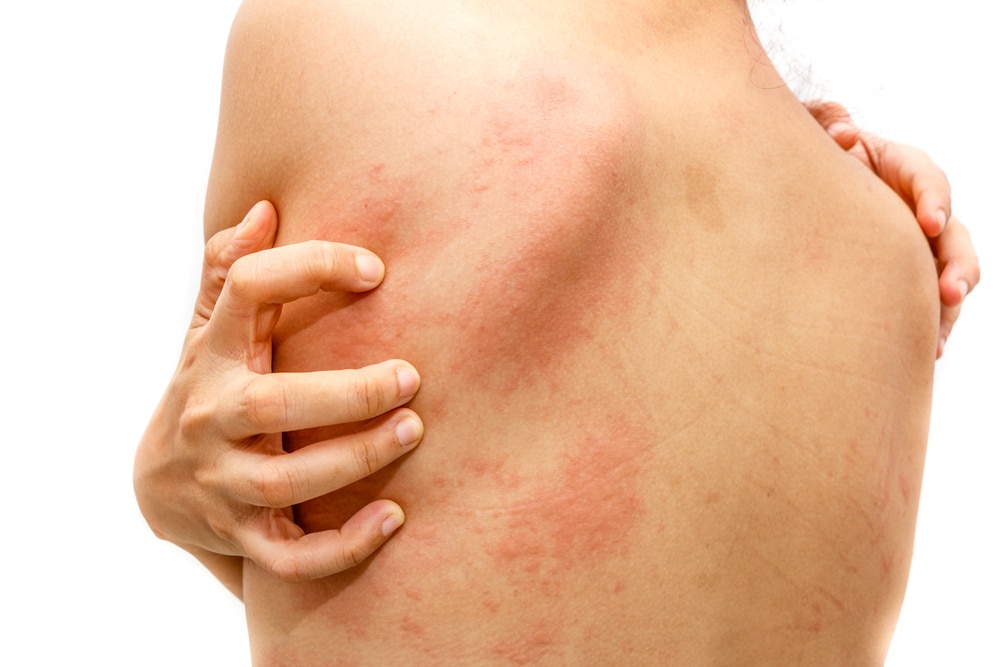
Overview
Urticaria, or hives, is a common condition that is characterized by red or pink “welts” appearing on the skin. These can vary in size, from small to very large, and can be extremely itchy. An individual welt often will come and go in less than 24 hours but new hives can occur elsewhere, therefore a patient often experience hives for days to weeks. Acute means short term (less than 6-8 weeks).
In 10% of cases, hives may be accompanied by deeper swelling of eyelids, lips, fingers, etc. known as angioedema. If you notice swelling in your throat and find it difficult to breathe, you should go to the Emergency Department as this could become a life-threatening problem.
What Causes Hives?
Hives result as the body overreacts to an irritated stimuli. In most cases the direct cause of hives is unknown or occurs after a recent viral infection. Hives can also result from an allergy to a certain substances that may include: antibiotics, certain foods, bee stings, and other uncommon causes.
Treatment
The swelling and itchiness associated with hives is caused by the rapid release of histamine from cells within the body. Therefore, we target our treatment to stop the release of histamine. We do this by implementing several different antihistamine medications. These medicines are very safe and, in the case of the OTC (no prescription needed) non-sedating antihistamines, we standardly use 4 x the normal dose. We recommend continuing on the treatment regimen daily until at least a week after the hives are gone. We utilize this treatment to buy time until the body can correct whatever caused the initial reaction. A common treatment regimen includes:
- Some combination of an OTC oral non-sedating antihistamine. Daily adult dosage of Zyrtec (cetirizine) 10 mg, Allegra (fexofenadine) 180 mg, or Claritin (loratadine) 10 mg. Generic or brand is fine. For example:
- Take 2 x Allegra or 2 Claritin in the morning and 2 x Zyrtec at night
- Take 2 x Zyrtec in the morning and 2 again at night
- Take 2 x Allegra in the morning and 2 again at night
- Take 2 x Claritin in the morning and 2 again at night
*some patients do well with just double or triple the daily dose
- In addition take a sedating antihistamine such as Benadryl 25-50 (or 75) mg OR a prescription sedating antihistamine 2-7 10 mg hydroxyzine (Atarax), 20-70 mg, at night to help with sleep.
- In addition take one 75 mg or 150 mg Zantac (ranitidine) in the morning and one at night. (This is an over the counter heartburn medicine that also has anti-histamine effects)
- Take one 10 mg montelukast daily (this is a prescription and is given if insurance covers it)
In addition, we sometimes prescribe a topical cortisone which may be mixed with an anti-itch lotion called Sarna to aid in the itch relief. Rarely we will prescribe oral steroids or give a steroid injection. These can help calm down itching and inflammation but are not as specific at getting at the base cause of controlling histamine release (therefore we try not to use just steroids as a first line treatment).