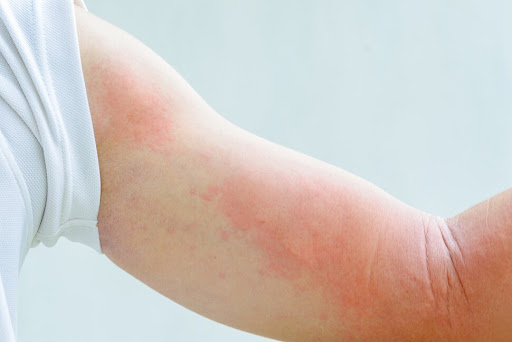
HIVES
Urticaria, or hives, is a common condition that is characterized by red or pink “welts” appearing on the skin. These can vary in size, from small to very large, and can be extremely itchy. An individual lesion often will come and go within 24 hours, but new hives can take its place; therefore a patient may experience hives for days or weeks. In some instances, the hives may be accompanied by deeper swelling of eyelids, lips, hands, and elsewhere. This is known as angioedema. If you notice swelling in your throat and find it difficult to breathe, you should go to the emergency room as this could become a life-threatening problem.
Hives result as the body overreacts to an irritant. In most cases the direct cause of hives is unknown or occurs after a recent viral infection. Hives can also result from an allergy to a certain substances that may include: antibiotics, certain foods, and bee stings. Getting medical treatment to prescribe medicine that will alleviate the symptoms is helpful in dealing with the discomfort.


